Understanding Cordyceps
Your Comprehensive Guide to Cordyceps Mushrooms
At The Botany Bay, we provide trustworthy information about botanicals so you can make informed decisions. Cordyceps is a unique genus of fungi traditionally used in herbal practices across Asia. Known for its unusual growth cycle and energizing reputation, Cordyceps has become a popular functional mushroom in modern wellness products.
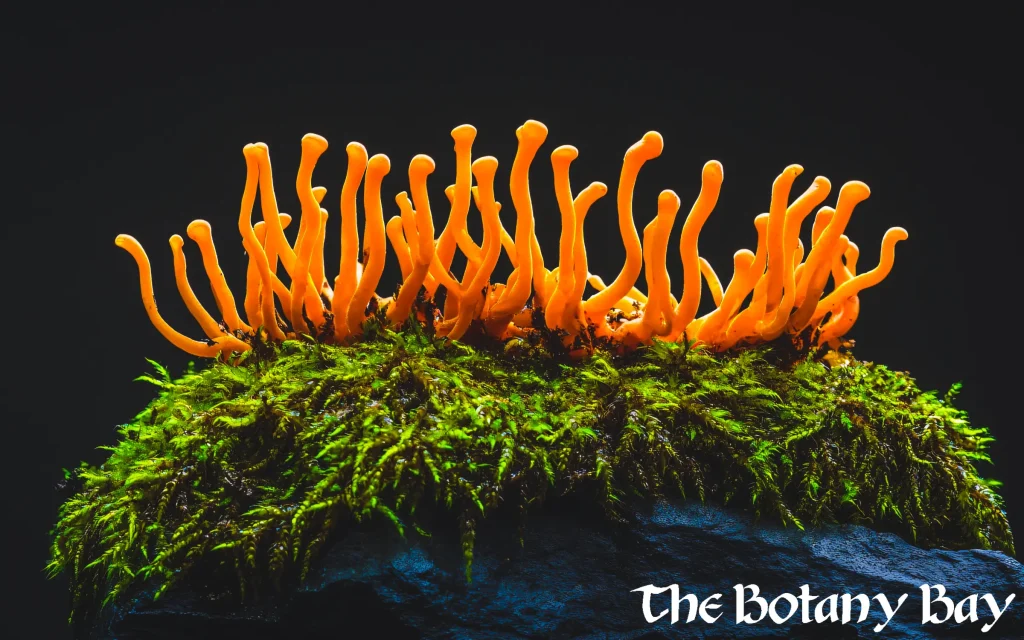
What Is Cordyceps?
Cordyceps refers to a group of parasitic fungi, with over 400 species identified. The most well-known are:
Cordyceps sinensis — Historically rare, once harvested from caterpillars in high-altitude regions of Tibet and China.
Cordyceps militaris — More common today, cultivated sustainably on plant-based substrates, making it widely available for supplements and extracts.
Unlike many mushrooms, Cordyceps does not form a traditional cap and stem. Instead, it produces elongated, club-like fruiting bodies.
How Cordyceps Works in the Body
Cordyceps is rich in polysaccharides, adenosine derivatives, and other bioactive compounds. The most studied is cordycepin, a nucleoside analog thought to influence energy pathways in the body.
Traditional use and modern research suggest Cordyceps may support:
Energy metabolism by influencing ATP production in cells
Oxygen utilization which may play a role in endurance
Immune function through its polysaccharide content
These effects are based on preliminary studies and historical use. More research is needed to fully understand its actions.

Did you know? Ancient Use
An unusual origin, caterpillar fungus. Flip to learn more.
Wild Cordyceps sinensis grows by infecting and mummifying caterpillars in the Himalayas — one of the reasons it was historically so rare and expensive.
Active Compounds
The key components, Cordycepin & Polysaccharides. Flip the box for more info.
Cordyceps contains cordycepin and unique beta-glucans, studied for their potential roles in energy metabolism and immune support.
Legal Status of Cordyceps
Cordyceps is legal in the United States and many countries worldwide. It is sold as a dietary supplement in the form of powders, capsules, tinctures, and extracts. It is not a controlled substance.
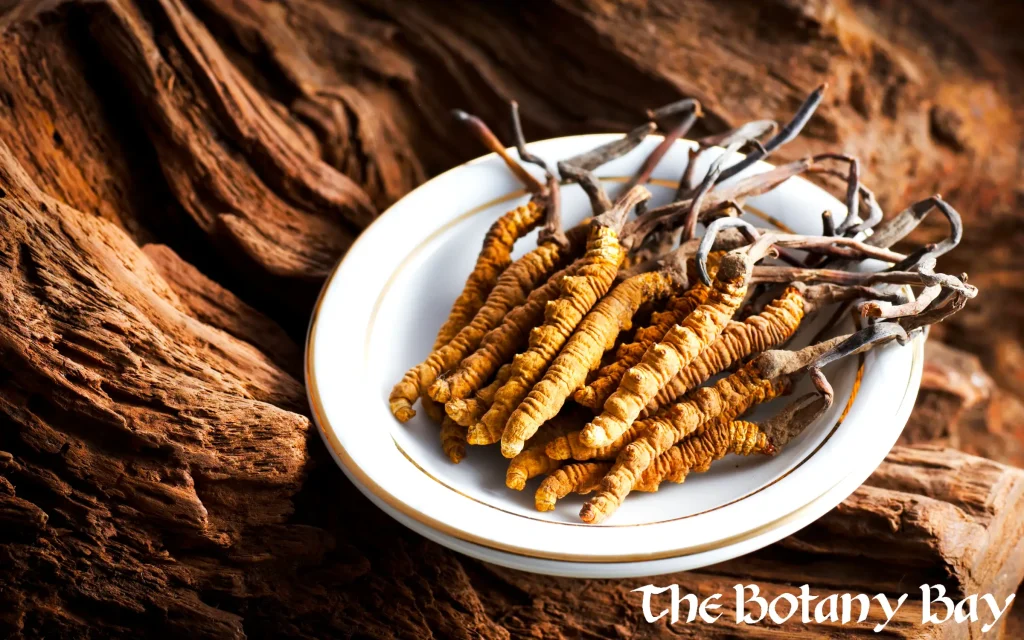

Reported Effects and Benefits
People who use Cordyceps products often describe:
A sense of sustained energy rather than a stimulant-like boost
Endurance support when taken before exercise
General wellness support when included in daily routines
These effects are anecdotal, and results can vary between individuals.
How to Use Cordyceps
Cordyceps is available in several supplement forms:
Capsules and tablets — Convenient, pre-measured servings
Powders — Added to smoothies, teas, or coffee blends
Tinctures and liquid extracts — Concentrated forms for flexible use
Functional mushroom blends — Often paired with Reishi, Lion’s Mane, or Turkey Tail
Because of its tough structure, Cordyceps is usually extracted rather than consumed raw.
Testing and Transparency
At The Botany Bay, all Cordyceps products we carry are:
Third-party lab tested for purity and identification
Screened for contaminants like heavy metals, pesticides, and microbes
Clearly labeled with species information (militaris vs. sinensis)
Compliance Disclaimer
This content is for educational purposes only and has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Cordyceps products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Always consult a healthcare provider before beginning any new supplement, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, or taking medications.
FAQs About Cordyceps
Is Cordyceps a psychedelic mushroom?
Which is better: Cordyceps sinensis or Cordyceps militaris?
Can I eat Cordyceps raw?
Why is wild Cordyceps so expensive?
NEWSLETTER
Sign up to our newsletter to keep updated with our latest offers and products.
© 2025 The Botany Bay All Rights Reserved
Disclaimer:
Some products sold by The Botany Bay are not scheduled under U.S. federal law but may be subject to state or local restrictions. The Botany Bay conducts due diligence and restricts orders to jurisdictions where these products are legal. Orders placed to prohibited areas will not be fulfilled. However, it remains the customer’s responsibility to ensure compliance with any applicable local, state, or international laws before purchasing. These products have not been evaluated by the FDA and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Kratom Disclaimer:
This product is not available for shipment to the following states: Alabama, Arkansas, Indiana, Louisiana, Rhode Island (until April 1, 2026), Vermont, and Wisconsin; or the following localities: Sarasota County (Florida); San Diego, Oceanside, Newport Beach, and unincorporated San Diego County (California); Alton, Jerseyville, Edwardsville, Glen Carbon, and Godfrey (Illinois); Denver, Monument, and Parker (Colorado); and Union, Alcorn, Lowndes, Monroe, and Tishomingo Counties, as well as the cities of Columbus, Oxford, Ridgeland, Corinth, Belmont, and Gluckstadt (Mississippi).
Cannabinoid Disclaimer:
This product is not available for shipment to states that restrict or ban hemp-derived cannabinoids, including Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Delaware, Hawaii, Idaho, Iowa, Mississippi, Montana, Nevada, New York, North Dakota, Rhode Island, Utah, and Vermont; or to jurisdictions with specific local prohibitions on psychoactive hemp derivatives (e.g., Delta-8, THCA).
Disambiguation Disclaimer: The Botany Bay is not affiliated with Botany Farms.
- 0 Items
- View Cart
